24 KiB
wireguard-manager
WireGuard Manager is an open-source web application written in Go that simplifies the management of a WireGuard VPN server. It provides a user-friendly web interface for administering server settings, managing VPN client configurations, and handling user accounts. Additionally, the project supports email notifications (via SMTP or SendGrid), secure session management, and configuration change detection.
Features
- Manage WireGuard server settings, VPN client configurations, and user accounts through an intuitive web interface.
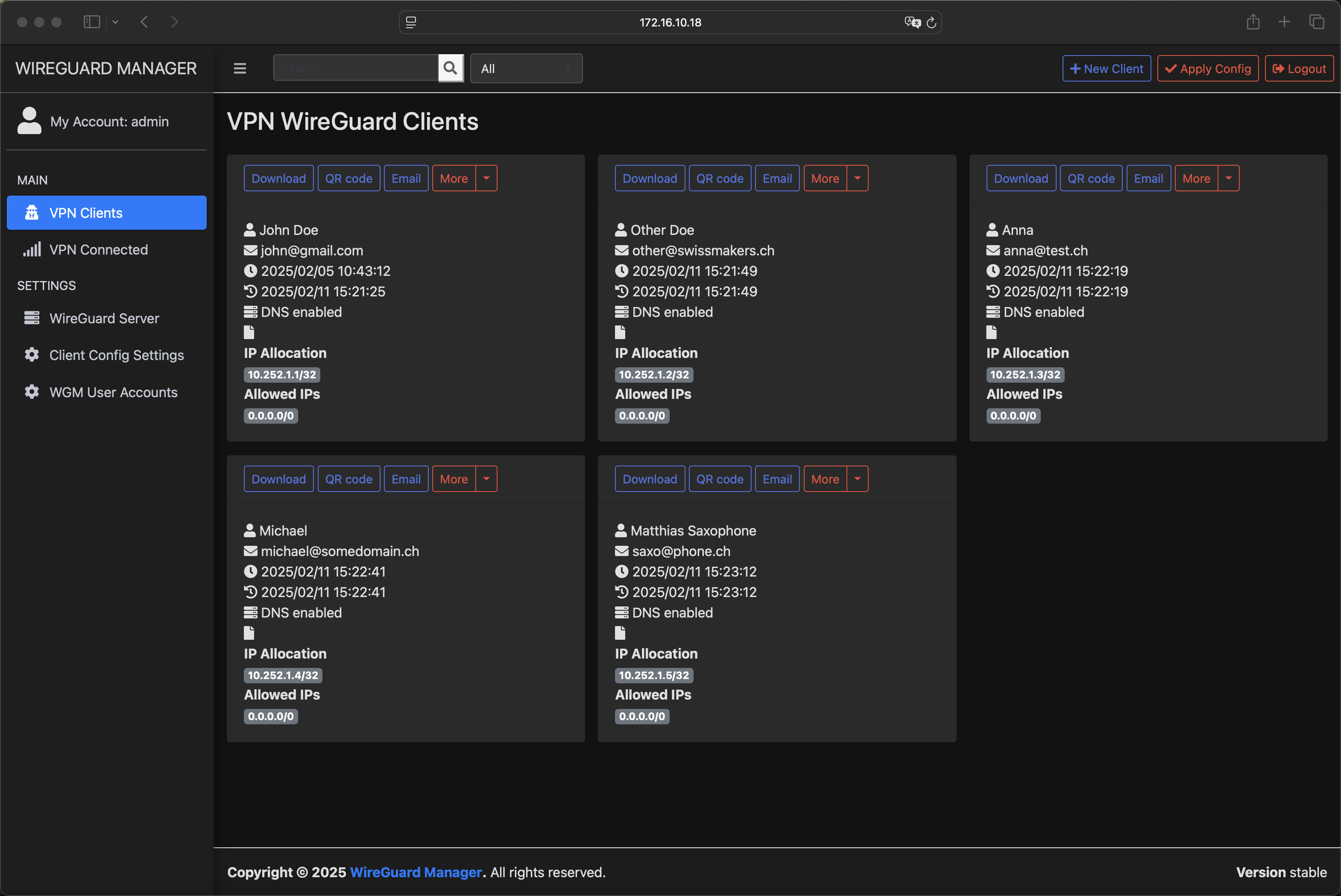
- Create, update, and delete VPN clients. Automatically generate client configurations and QR codes.
- Send client configuration files via email using either SMTP or SendGrid.
- Secure Session Management: Sessions are managed using Gorilla Sessions with a persisted session secret stored in the JSON DB, ensuring that session cookies remain valid across restarts.
- Configuration Change Detection: Polls for configuration changes and prompts the admin to apply new configurations via an “Apply Config” button.
- A dark mode user interface with responsive design for an improved user experience.
Note: The default login username/password is
admin/swissmakers. Please change it in your environment for production.
Table of Contents
- Installation Example on CentOS/RHEL 9 (Manual Setup)
- Environment Variables
- Auto-Restarting WireGuard
- Build From Source
- License
Installation Example on CentOS/RHEL 9 (Manual Setup)
Below is a step-by-step guide demonstrating how to set up wireguard-manager manually on a CentOS/RHEL 9 system, along with WireGuard and systemd units for auto-restart.
Prerequisites
- A fresh or existing CentOS/RHEL 9 server
- Root or
sudoprivileges - Networking available for package installation
Steps
-
Update the system:
dnf update -y -
Enable Node.js module (if needed for asset building):
dnf module enable nodejs:22 -y -
Install required packages:
dnf install -y \ wireguard-tools \ git \ vim \ container-tools \ golang \ yarnpkg \ npm -
Clone
wireguard-managerrepository:git clone https://github.com/swissmakers/wireguard-manager.git /opt/wireguard-manager -
(Optional) Install specific Golang RPMs:
If your environment needs a newer version of Go than provided by default, you can grab the RPMs (example shown below) or use the already downloaded ones inside "./dev/go-rpm" folder inside this project.mkdir -p ./dev/go-rpms && cd ./dev/go-rpms wget https://rpmfind.net/linux/centos-stream/9-stream/AppStream/x86_64/os/Packages/golang-race-1.23.2-1.el9.x86_64.rpm wget https://rpmfind.net/linux/centos-stream/9-stream/AppStream/x86_64/os/Packages/golang-bin-1.23.2-1.el9.x86_64.rpm wget https://rpmfind.net/linux/centos-stream/9-stream/AppStream/x86_64/os/Packages/golang-src-1.23.2-1.el9.noarch.rpm wget https://rpmfind.net/linux/centos-stream/9-stream/AppStream/x86_64/os/Packages/golang-1.23.2-1.el9.x86_64.rpm dnf install -y ./*.rpm -
Create a dedicated WireGuard user and config:
useradd -m -r -s /bin/false -d /var/lib/wireguard wireguard touch /etc/wireguard/wg0.conf -
Adjust permissions for the WireGuard configuration:
chmod 750 /etc/wireguard chown root:wireguard /etc/wireguard setfacl -m u:wireguard:rx /etc/wireguard setfacl -m u:wireguard:rw /etc/wireguard/wg0.conf -
Create/modify the environment configuration:
For example, place it in/opt/wireguard_environment.conf(or any path you prefer):vim /opt/wireguard_environment.confSample contents:
BASE_PATH="/" BIND_ADDRESS="0.0.0.0:5000" SESSION_SECRET="**********************************" WGM_USERNAME="admin" WGM_PASSWORD="**********************************" WGM_ENDPOINT_ADDRESS="vpn.example.com" WGM_DNS="8.8.8.8" WGM_MTU="1450" WGM_PERSISTENT_KEEPALIVE="15" WGM_CONFIG_FILE_PATH="/etc/wireguard/wg0.conf" # WGM_LOG_LEVEL="DEBUG" # WG_CONF_TEMPLATE= EMAIL_FROM_ADDRESS=noreply@example.com EMAIL_FROM_NAME=noreply # SENDGRID_API_KEY= SMTP_HOSTNAME=smtp.office365.com SMTP_PORT=587 SMTP_USERNAME=noreply@example.com SMTP_PASSWORD="**********************************" SMTP_AUTH_TYPE=LOGIN SMTP_ENCRYPTION=STARTTLS -
Create the systemd service unit for
wireguard-manager:vim /etc/systemd/system/wireguard-manager.serviceExample service:
[Unit] Description=WireGuard Manager After=network.target ConditionPathExists=/var/lib/wireguard [Service] Type=simple User=wireguard Group=wireguard CapabilityBoundingSet=CAP_DAC_READ_SEARCH CAP_NET_ADMIN CAP_NET_RAW AmbientCapabilities=CAP_DAC_READ_SEARCH CAP_NET_ADMIN CAP_NET_RAW WorkingDirectory=/opt/wireguard-manager EnvironmentFile=/opt/wireguard_environment.conf ExecStart=/opt/wireguard-manager/wireguard-manager Restart=on-failure RestartSec=10 [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target -
Open firewall ports (if your setup requires external access to port 5000):
firewall-cmd --add-port=5000/tcp --permanent firewall-cmd --reload10.1. Also pre-define the later used rich-rule for VPN traffic from your VPN interface to your LAN:
firewall-cmd --permanent --add-rich-rule='rule family="ipv4" source address="10.8.0.0/24" masquerade' firewall-cmd --reload -
Build the
wireguard-managerand chown to right user:cd /opt/wireguard-manager ./prepare_assets.sh go build -o wireguard-manager chown -R wireguard:wireguard /opt/wireguard_environment.conf /opt/wireguard-manager/ /etc/wireguard/wg0.conf -
If you also using SELinux keep that in mind as well. There are some additionals settings needed. (Will be documented later.)
-
Enable and start
wireguard-manager:systemctl daemon-reload systemctl enable wireguard-manager.service --now systemctl status wireguard-manager.service13.1 On SELinux enabled servers it will fail here. You need to do the following:
restorecon -Rv /opt/ setsebool -P domain_can_mmap_files on systemctl restart wireguard-manager.service systemctl status wireguard-manager.service -
(Optional) Set up watchers for auto-restarting WireGuard
See Auto-Restarting WireGuard below for details on usingsystemdpath units or other methods.
Environment Variables
Below is a table of commonly used environment variables for configuring wireguard-manager. These can be set in your environment file (e.g., /opt/wireguard_environment.conf) or as Docker environment variables.
| Variable | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|
| BASE_PATH | Subpath on your reverse proxy’s virtual host (e.g. /wireguard) |
(none) |
| PROXY | When true, uses X-FORWARDED-FOR headers for logging. Accepts boolean (0, f, false, 1, t, true). |
false |
| BIND_ADDRESS | Address and port for the web interface. Or use unix:///absolute/path.sock for a Unix socket. |
0.0.0.0:80 |
| SESSION_SECRET | Secret key to encrypt session cookies. Set to a secure random value. | (none) |
| SESSION_SECRET_FILE | Path to a file containing the session secret. Takes effect only if SESSION_SECRET is unset. |
(none) |
| SESSION_MAX_DURATION | Maximum time in days for a "remembered" session refresh (otherwise 7 days). | 90 |
| SUBNET_RANGES | Address subdivision ranges. Format: SR1:10.0.1.0/24; SR2:10.0.2.0/24,10.0.3.0/24 (each CIDR must be valid in the server interface). |
(none) |
| WGM_USERNAME | Admin username for the login page, used only for the initial database creation. | admin |
| WGM_PASSWORD | Admin password (plaintext, will be hashed on first run). Only for initial db creation. | admin |
| WGM_PASSWORD_FILE | Path to a file containing the admin password. Takes effect only if WGM_PASSWORD is unset. |
(none) |
| WGM_PASSWORD_HASH | Pre-hashed admin password (alternative to WGM_PASSWORD). |
(none) |
| WGM_PASSWORD_HASH_FILE | Path to a file containing a pre-hashed password. Takes effect only if WGM_PASSWORD_HASH is unset. |
(none) |
| WGM_ENDPOINT_ADDRESS | Default WireGuard endpoint (e.g., vpn.mydomain.com:51820). If omitted, wireguard-manager attempts to guess your public IP. |
(system-detected public IP) |
| WGM_FAVICON_FILE_PATH | Path to a custom favicon file for the web interface. | (embedded WireGuard logo) |
| WGM_DNS | Comma-separated DNS servers used by clients. | 1.1.1.1 |
| WGM_MTU | Default MTU. | 1450 |
| WGM_PERSISTENT_KEEPALIVE | Default keepalive for WireGuard peers. | 15 |
| WGM_FIREWALL_MARK | Default firewall mark for WireGuard. | 0xca6c |
| WGM_TABLE | Default table value for WireGuard. Can be auto, a number, or off. |
auto |
| WGM_CONFIG_FILE_PATH | Default location for the wg0.conf file. |
/etc/wireguard/wg0.conf |
| WGM_LOG_LEVEL | Log level. One of DEBUG, INFO, WARN, ERROR, OFF. |
INFO |
| WG_CONF_TEMPLATE | Custom wg.conf template file. See the default template. |
(none) |
| EMAIL_FROM_ADDRESS | Sender email address when sending client configs. | (none) |
| EMAIL_FROM_NAME | Sender name for emails. | WireGuard Manager |
| SENDGRID_API_KEY | SendGrid API key for sending emails. | (none) |
| SENDGRID_API_KEY_FILE | Path to a file containing the SendGrid API key. Takes effect only if SENDGRID_API_KEY is unset. |
(none) |
| SMTP_HOSTNAME | Hostname or IP address of the SMTP server. | 127.0.0.1 |
| SMTP_PORT | SMTP server port. | 25 |
| SMTP_USERNAME | SMTP username. | (none) |
| SMTP_PASSWORD | SMTP password. | (none) |
| SMTP_PASSWORD_FILE | Path to a file containing the SMTP password. Takes effect only if SMTP_PASSWORD is unset. |
(none) |
| SMTP_AUTH_TYPE | SMTP authentication type: PLAIN, LOGIN, or NONE. |
NONE |
| SMTP_ENCRYPTION | Encryption type: NONE, SSL, SSLTLS, TLS, or STARTTLS. |
STARTTLS |
| SMTP_HELO | Hostname to use for SMTP HELO. | localhost |
Defaults for Server Configuration
Variables controlling the initial server configuration in the database:
| Variable | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|
| WGM_SERVER_INTERFACE_ADDRESSES | Server interface addresses, comma-separated. For example: 10.252.1.0/24 |
10.252.1.0/24 |
| WGM_SERVER_LISTEN_PORT | Server’s WireGuard listen port. | 51820 |
| WGM_SERVER_POST_UP_SCRIPT | Script to run after WireGuard interface goes up. | (none) |
| WGM_SERVER_POST_DOWN_SCRIPT | Script to run after WireGuard interface goes down. | (none) |
Defaults for New Clients
Variables controlling the initial defaults for new client creation in the UI:
| Variable | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|
| WGM_DEFAULT_CLIENT_ALLOWED_IPS | Allowed IPs, comma-separated (e.g., 0.0.0.0/0) |
0.0.0.0/0 |
| WGM_DEFAULT_CLIENT_EXTRA_ALLOWED_IPS | Extra Allowed IPs, comma-separated. | (none) |
| WGM_DEFAULT_CLIENT_USE_SERVER_DNS | Whether to use server DNS by default (boolean) | true |
| WGM_DEFAULT_CLIENT_ENABLE_AFTER_CREATION | Whether to enable the client immediately after creation (boolean) | true |
Docker-Only Variables
These variables only apply when running wireguard-manager in a Docker container:
| Variable | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|
| WGM_MANAGE_START | Start/stop WireGuard when the container starts/stops (replaces wg-quick@wg0 service). |
false |
| WGM_MANAGE_RESTART | Automatically restart WireGuard when you click “Apply Config” in the UI. | false |
| WGM_MANAGE_RELOAD | Use wg syncconf wg0 /path/to/conf to dynamically reload the config without a full interface restart. |
false |
Auto-Restarting WireGuard
wireguard-manager generates and updates the wg0.conf (or your chosen interface file), but does not, by itself, restart the WireGuard service. Below are optional methods to watch for changes and automatically restart or reload WireGuard.
Using systemd
1. Create a systemd "path" unit and "service" unit
-
Create the service unit
/etc/systemd/system/wgm.service:[Unit] Description=Restart WireGuard After=network.target [Service] Type=oneshot ExecStart=/usr/bin/systemctl restart wg-quick@wg0.service [Install] RequiredBy=wgm.path -
Create the path unit
/etc/systemd/system/wgm.path:[Unit] Description=Watch /etc/wireguard/wg0.conf for changes [Path] PathModified=/etc/wireguard/wg0.conf [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target -
Enable and start the path + service:
systemctl daemon-reload systemctl enable wgm.{path,service} systemctl start wgm.{path,service}
When wg0.conf changes, systemd triggers wgm.service, which restarts the wg-quick@wg0 interface.
Using OpenRC
-
Create a script
/usr/local/bin/wgm:#!/bin/sh wg-quick down wg0 wg-quick up wg0Make it executable:
chmod +x /usr/local/bin/wgm -
Create an OpenRC service
/etc/init.d/wgm:#!/sbin/openrc-run command=/sbin/inotifyd command_args="/usr/local/bin/wgm /etc/wireguard/wg0.conf:w" pidfile=/run/${RC_SVCNAME}.pid command_background=yesMake it executable:
chmod +x /etc/init.d/wgm -
Enable the service:
rc-service wgm start rc-update add wgm default
Using Docker
Set the following environment variables in your Docker container to manage the WireGuard interface directly:
-
WGM_MANAGE_START=true
The container will bringwg0up when starting and bring it down when stopping. This can replace thewg-quick@wg0system service. -
WGM_MANAGE_RESTART=true
The container will automatically restartwg0when you click “Apply Config” in the UI. -
WGM_MANAGE_RELOAD=true
The container will attempt awg syncconfreload instead of a full restart when you click “Apply Config”.
Important: Make sure your container has
--cap-add=NET_ADMINso that it can manipulate network interfaces.
Build From Source
Build Docker Image
From the project root directory:
docker build \
--build-arg GIT_COMMIT=$(git rev-parse --short HEAD) \
-t wireguard-manager .
Or using docker-compose:
docker compose build \
--build-arg GIT_COMMIT=$(git rev-parse --short HEAD)
An official container image is also available on Docker Hub:
docker pull swissmakers/wireguard-manager
Build Binary File
- Prepare the assets:
cd /opt/wireguard-manager ./prepare_assets.sh - Build:
go build -o wireguard-manager - Run the newly built binary:
./wireguard-manager
License
This project is licensed under the MIT License.